Bitcoin Runes, another token standard coming out of the Bitcoin network (after BRC-20) has hit the market on 20th April 2023 just at the time of Bitcoin halving. Runes were created by Casey Rodarmor (creator of Bitcoin ordinals) and are based on the Ordinals Theory.
The protocol helps in the creation and management of memecoins and degens in a way similar to Solana.
Table of Contents
How Bitcoin Ordinals Helped Create Surge in Bitcoin Miner Revenues?
After the introduction of Bitcoin Ordinals, we saw a huge interest in them from the crypto community. Introduced in December 2022, Ordinals saw a huge boost near May 2023. The number of inscriptions (creation of Ordinals) touched as high as 400k per day.
The creation of each ordinal was done by inscribing information onto a Satoshi, which was the smallest unit of Bitcoin (1 Bitcoin = 100 million Satoshis).

Consequently, there was also a boost in the fees paid. Each Ordinals was basically created on a single Satoshi but their transaction fees was similar to transferring ordinary Bitcoins because both of them introduce similar changes in the Bitcoin blockchain.
Note: Fees in blockchains are calculated based on how much data you are adding to the blockchain.
Let us simplify it with an hypothetical example. Assume that for the transfer of 1 Bitcoin, it consumes 100 MB of data, and costs $10. So for the transfer of 1 Satoshi it would require 1 byte of data, and a fee of $0.00001. However, since a ordinal is created with adding more data onto a Satoshi, its size increases, to say 10 MB. Hence, the fees could be around $1 (1/10th of Bitcoin in size). But the Satoshi still remains a Satoshi, its value is the same but its transfer fee has increased 10 million times.
This is how the fee has increased after the introduction of Ordinals.
Decoding Miner Revenue Increase Due to Ordinals
Now an increased fee would also mean an increase in miner revenues as each Bitcoin Ordinal would have to go through the verification process similar to an ordinary transaction.

All in all, Bitcoin Ordinals helped miners make approximately $451 million in just fees. Also the value of miner stocks went up by 100%-300%.
Will the Same Story Repeat for Bitcoin Runes?
Yes, let me explain why. Casey Rodarmor has created Bitcoin Runes to help developers create memecoins which are easier to create, deploy and manage.
We expect Bitcoin Runes to have a similar or even a stronger performance than Bitcoin Ordinals. The reason is due to the high demand in the Memecoin markets.
Lately, memecoins have been the largest gainers in the crypto markets. Traditional memecoins like Dogecoin and Shiba Inu, have been trading at nearly 2x-3x prices as compared to the past year. New memecoins like Bonk, Pepe, dogwifhat and many others have also garnered massive number of users.
The combined net worth of all memecoins stands at $56.8 billion as of 24th April 2024.
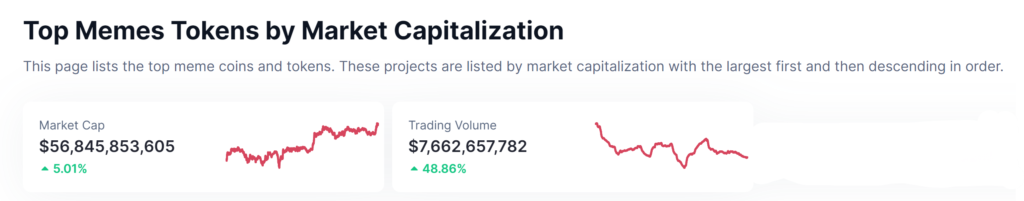
Now, if the same cryptocurrencies will be created on Bitcoin, they could fetch far more users than any other blockchain. The unmatched security of Bitcoin Network would make these cryptocurrencies more safe than other blockchain.
Runes vs Ordinals
Bitcoin Ordinals which were first seen in December 22, 2023 were intended to bring NFT like capabilities to the Bitcoin blockchain. They were created by Casey Rodarmor and used unspent UTXOs to create new cryptocurrencies.
On the other hand Bitcoin Ordinals are Satoshis on which information is inscribed.
Detailed Article on Bitcoin Runes: What are Bitcoin Runes? How Do They Work?




