Ethereum ETFs Trading at 25% Undervaluation
Ethereum ETFs lack staking benefits, which dissuades buyers. If they included staking rewards, interest would likely increase, pending SEC approval.
Ethereum ETFs lack staking benefits, which dissuades buyers. If they included staking rewards, interest would likely increase, pending SEC approval.
Ethereum has been behaving irrationally despite having the following things to its advantage. Ethereum had the highest blockchain revenue in 2024 ($2.5 billion), beating all other cryptocurrencies like Tron, Bitcoin, and Solana. The number of dApps on Ethereum is far…

In Ethereum, Gas War means a competitive situation where senders compete for gas fee to get their transactions executed in priority.
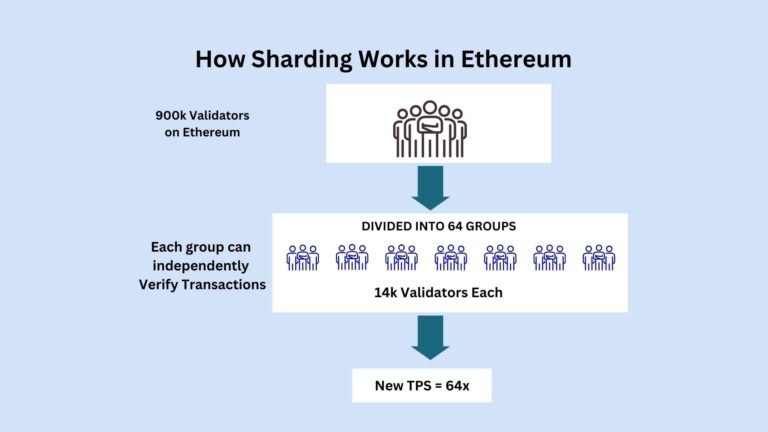
Sharding is the process of breaking a blockchain's total no. of validators into smaller groups called "Shards". Each shard has its own unique set of validators.